I am not a developer and have been looking for a reason to use WSL for a while and found a good use case to Terraform using VS Code on Linux. In my opinion Hashicorp's Terraform is the de facto choice in the infrastructure as code space just like Kubernetes is for container orchestration. Use this Terraform and Azure DevOps tutorial to start automating infrastructure as code. Follow along to build configuration and variable files for an Azure storage account, commit them in a repo, then set up a YAML pipeline for build and release. (Optional) Visual Studio Code with the Terraform extension; Installing Terraform on Windows. To leverage the power of Terraform, you must first get it installed on your operating system of choice. In this article, I'm going to be focusing on Windows. But know that Terraform can run on other operating systems. Microsoft Visual Studio Code and the Azure Resource Manager Template Extension for Visual Studio Code; Terraform and Azure PowerShell - the Azure Cloud Shell interactive shell has both pre-installed; and; A Microsoft Azure account. Azure Resource Manager templates. ARM templates are JSON documents that define each aspect of the IT.
- Visual Studio Code Terraform Aws
- Visual Studio Code Vs Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code Snippets
- Visual Studio Code Terraform Init
- Visual Studio Code Terraform 12
- Visual Studio Code Terraform 12
I'm becoming a huge fan of Terraform, having started using it at work to manage our AWS environment and using it more recently with Virtual Design Master. When working with Terraform there are a few simple things that can make a big difference, using a good development environment and using a source code repository. These are obvious things for any developer but as an infrastructure guy I've grown into using them as I've used Terraform. The following is how to get all of this setup on Windows.
Installing Terraform
Installing Terraform is simple – its a self contained binary which needs adding to your PATH variable.
- Download Terraform from https://www.terraform.io/downloads.html
- Unzip it anywhere, but as we are going to add this to the PATH environment variable, make it somewhere fairly permenant. For me thats c:userschristoolsterraform
- Add the location where you unzipped Terraform to your PATH environment variable. To that, hit Start, type environment and select the result shown as ‘Edit the system environment variables.
- Click the ‘Environment Variables…' button to the bottom right of the settings box that appears.
- Under System variables select Path and click on Edit
- Click New and enter the path to where you unzipped terraform.exe.
- Click OK, then OK, then OK.
- Open up command prompt and type terraform. You should see the terraform help appear.
Installing Visual Studio Code with the Terraform Extension
- Download Visual Studio Code (VSC) from https://code.visualstudio.com/download
- Run the installer, tick to add an option to open folders with VSC
- Installer will complete and VSC can now be opened from the Start Menu.
- Open VSC
- Click the extension button from the left hand menu
- Type terraform in the search bar
- Click the green ‘Install' button next to the extension from Mikael Olenfalk
- That's it, you now have a development environment which also includes syntax highlighting and automatic formatting in Terraform files.
Setting up Git in VSC
Git integration is included out of the box with VSC but we do need to install Git for Windows first to install the git.exe executable VSC uses.
- Download Git from https://git-scm.com/download/win
- Run the Git installer. There are lots of options for the install of Git but the defaults are fine. For VSC, ensure the options ‘Use Git from Windows Command Prompt' and ‘Enable Git Credential Manager' are selected so the VSC can find git.exe and secure credential storage.
- Setup some basic required user config for git. Open command prompt and run the following commands;git config –global user.name 'Your Name'
Once Git is installed and configured, we need to create a folder and initialise it as Git repository.
- Create a folder for this Terraform project. Terraform projects (technically know as modules) live within a folder so create something specific for this tutorial. For me this is c:userschrisprojectsterraform-tutorial.
- Open VSC
- Click File > Open Folder
- Open the folder you created in Step 1
- Click View > SCM
- At the top of middle narrow pane, click ‘Initialize Repository'.
Thats Git setup for this project – easy, right? Lets create our first file and commit the changes
- Click File > New File
- Click File > Save
- As the file has not been saved before, the Save As dialog opens. It should be in the same folder as we opened earlier on but double check. Name the file main.tf and click save.
- The Source Control icon on the left hand pane should change to show 1 uncommitted change for the repository.
- Click on Source Control icon.
- Hover of the main.tf file and click the ‘+' to stage the file. This means it will be included in the next commit, allowing you to decide which files are committed and which files are not.
- Enter a short message to describe the commit and hit the ‘tick' to perform the commit.
From now on, as you update files in the folder, you should get into the habit of periodically staging and committing your changes.
A good place to start with Terraform is to follow Hashicorp's Getting Started guide, which can be found here; https://www.terraform.io/intro/getting-started/build.html
That's the basics of git, terraform and VSC covered!
In the infrastructure as code (IaC) space, one of the most useful tools to come out in the last several years is HashiCorp's Terraform. The ability to version infrastructure, automate provisioning of resources, and execute across different cloud vendors is huge for any DevOps and automation workflows.
One use-case for Terraform is in CI/CD. Terraform allows you to:
Get your AnyDesk subscription! We're happy to help you find the perfect solution for your needs. General Support. Do you have any feedback, generic questions or inquiry? We'd love to hear from you. Please contact us. Subscribe to our Newsletter. AnyDesk allows you to establish remote desktop connections in Windows 10 and opens up unprecedented possibilities of collaborating online and administrating your IT network. With AnyDesk, you can work remotely from everywhere! Dynamic Performance for Smooth Windows Remote Access. AnyDesk ensures secure and reliable remote desktop connections for IT professionals and on-the-go individuals alike. Start your 14 day trial today. Work from Home Learn more. 300+ million downloads worldwide. 400+ million sessions per month. Contact AnyDesk. If you have problems concerning the software (connection errors etc.), please use this contact form! Anydesk details. AnyDesk outputs a log/trace file while running, that can be utilized to diagnose problems. Some errors occur without causing an immediate crash. Those may lead to a malicious behaviour. It is therefore quite helpful if you report issues including some documentation as well as the trace files from both participating devices.
- create a testing environment
- deploy an application
- run integration tests
- destroy the testing environment
All of the steps are performed automatically too. And no data center required!
Prerequisites
This article is a walkthrough on getting Terraform up and running on Windows. If you'd like to follow along, please be sure you have the following prerequisites in place.
- A Windows 10 device
- An AWS Account
- The AWS CLI installed and configured on that device. You can learn how to install it here and how to configure it here.
- (Optional) Visual Studio Code with the Terraform extension
Installing Terraform on Windows
To leverage the power of Terraform, you must first get it installed on your operating system of choice. In this article, I'm going to be focusing on Windows. But know that Terraform can run on other operating systems. If you're not on Windows, take a look at the installation documentation.
The Hard Way
If you can't use a package manager or you want to understand how the installation process works, you can install Terraform manually. You can install Terraform by downloading the binary and adding it to the system path environment variable. If this looks intimidating, I assure you there's an easier way to do it you'll learn in the next section.
- Download the appropriate version of Terraform from HashiCorp's download page. In my case, it's the Windows 64-bit version.
- Make a folder on your C: drive where you can put the Terraform executable. I prefer to place installers in a subfolder (e.g. C:tools) where you can put binaries.
- After the the download finishes, go find it in File Explorer. Extract the zip file to the folder you created in step 2.
- Open your Start Menu and type in 'environment' and the first thing that comes up should be Edit the System Environment Variables option. Click on that and you should see this window.
5. Click on Environment Variables… at the bottom and you'll see this:
6. Under the bottom section where it says System Variables, find one called Path and click edit. You'll then see a list of where to find the binaries that Windows might need for any given reason.
7. Click New and add the folder path where terraform.exe is located to the bottom of the list. It should look like this when you finish.
8. Click OK on each of the menus you've opened up until there's no more left.
9. To make sure that Windows detects the new path, open a new CMD/PowerShell prompt and enter refreshenv.
10. Verify the installation was successful by entering terraform --version. If it returns a version, you're good to go.
The Easy Way
Phew, that was a lot of work! That would be awful to do every time you had to install new software on your device. Let's use a package manager instead. There are a few out package managers you can use to install Terraform on Windows. For Windows, my favorite is Chocolatey. It makes installing, removing and updating software as simple as a one-line command, and Terraform is no exception to that.
Visual Studio Code Terraform Aws
To install Terraform with Chocolatey, do the following steps:
- Open a CMD/PowerShell prompt as an administrator and install Chocolatey using the command from their install page.
- Once that is complete, run
choco install terraform. If you like, you can also put-yon the end to auto-agree to installing it on your device.
After that command runs, you will get something like this:
3. Verify the installation was successful by entering terraform --version.
The Linux Way
I can almost hear what you're thinking. Wait a minute Chris, didn't you say this was going to cover installing Terraform on Windows?
Yes, and it still is. But one of the features on Windows 10 is the Windows for Linux Subsystem, or WSL. This allows you to run Linux commands on Windows.
- Install WSL. I'm not going to go in depth on how to install and set up WSL here, but if you want to follow along and don't have it set up already. A TechSnips snip I did on this topic can be found below.
2. In your WSL shell, run apt-get install unzip You'll need this to extract the Terraform binaries later.
3. Download Terraform by running wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.12.6/terraform_0.12.6_linux_amd64.zip. Remember to replace the version and architecture with the one that best fits your device. You can find the full list of Terraform Releases here.
4. Run unzip terraform_0.12.6_linux_amd64.zip terraform to unzip the contents of the zip into a folder called terraform.
5. Once the ZIP file is uncompressed, you'll need to move it somewhere accessible by the system path. Fortunately, Linux has a folder that users can add binaries to by default. Move the Terraform binary there by running mv terraform /usr/local/bin/. The /usr/local/bin folder is already set in your system path.
6. Verify the installation was successful by running terraform --version.
Automating an AWS EC2 Instance with Terraform
Now that you have installed Terraform, you can begin using it. In this post, I'm going to demonstrate building with a simple AWS EC2 instance. But know Terraform can provision hundreds of different types of infrastructure.
To get started, you'll first need a directory to run the Terraform scripts from. It's important to have a separate directory for each environment. At the time I'm writing this, Terraform doesn't have a way to filter what it runs. It will run every script in your current working directory.
Setting Up a TF Script
- In your cmd or PowerShell console ran as administrator, run
mkdir hello-terraformthencd ./hello-terraform - Once you have a directory, you'll need a Terraform script. Below is an example of one you can use. This is a typical Terraform script using the AWS provider to create an AWS instance resource.
If you'd like the entire script, copy it below. If you want to understand what this script is doing, read on below.
All of the steps are performed automatically too. And no data center required!
Prerequisites
This article is a walkthrough on getting Terraform up and running on Windows. If you'd like to follow along, please be sure you have the following prerequisites in place.
- A Windows 10 device
- An AWS Account
- The AWS CLI installed and configured on that device. You can learn how to install it here and how to configure it here.
- (Optional) Visual Studio Code with the Terraform extension
Installing Terraform on Windows
To leverage the power of Terraform, you must first get it installed on your operating system of choice. In this article, I'm going to be focusing on Windows. But know that Terraform can run on other operating systems. If you're not on Windows, take a look at the installation documentation.
The Hard Way
If you can't use a package manager or you want to understand how the installation process works, you can install Terraform manually. You can install Terraform by downloading the binary and adding it to the system path environment variable. If this looks intimidating, I assure you there's an easier way to do it you'll learn in the next section.
- Download the appropriate version of Terraform from HashiCorp's download page. In my case, it's the Windows 64-bit version.
- Make a folder on your C: drive where you can put the Terraform executable. I prefer to place installers in a subfolder (e.g. C:tools) where you can put binaries.
- After the the download finishes, go find it in File Explorer. Extract the zip file to the folder you created in step 2.
- Open your Start Menu and type in 'environment' and the first thing that comes up should be Edit the System Environment Variables option. Click on that and you should see this window.
5. Click on Environment Variables… at the bottom and you'll see this:
6. Under the bottom section where it says System Variables, find one called Path and click edit. You'll then see a list of where to find the binaries that Windows might need for any given reason.
7. Click New and add the folder path where terraform.exe is located to the bottom of the list. It should look like this when you finish.
8. Click OK on each of the menus you've opened up until there's no more left.
9. To make sure that Windows detects the new path, open a new CMD/PowerShell prompt and enter refreshenv.
10. Verify the installation was successful by entering terraform --version. If it returns a version, you're good to go.
The Easy Way
Phew, that was a lot of work! That would be awful to do every time you had to install new software on your device. Let's use a package manager instead. There are a few out package managers you can use to install Terraform on Windows. For Windows, my favorite is Chocolatey. It makes installing, removing and updating software as simple as a one-line command, and Terraform is no exception to that.
Visual Studio Code Terraform Aws
To install Terraform with Chocolatey, do the following steps:
- Open a CMD/PowerShell prompt as an administrator and install Chocolatey using the command from their install page.
- Once that is complete, run
choco install terraform. If you like, you can also put-yon the end to auto-agree to installing it on your device.
After that command runs, you will get something like this:
3. Verify the installation was successful by entering terraform --version.
The Linux Way
I can almost hear what you're thinking. Wait a minute Chris, didn't you say this was going to cover installing Terraform on Windows?
Yes, and it still is. But one of the features on Windows 10 is the Windows for Linux Subsystem, or WSL. This allows you to run Linux commands on Windows.
- Install WSL. I'm not going to go in depth on how to install and set up WSL here, but if you want to follow along and don't have it set up already. A TechSnips snip I did on this topic can be found below.
2. In your WSL shell, run apt-get install unzip You'll need this to extract the Terraform binaries later.
3. Download Terraform by running wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.12.6/terraform_0.12.6_linux_amd64.zip. Remember to replace the version and architecture with the one that best fits your device. You can find the full list of Terraform Releases here.
4. Run unzip terraform_0.12.6_linux_amd64.zip terraform to unzip the contents of the zip into a folder called terraform.
5. Once the ZIP file is uncompressed, you'll need to move it somewhere accessible by the system path. Fortunately, Linux has a folder that users can add binaries to by default. Move the Terraform binary there by running mv terraform /usr/local/bin/. The /usr/local/bin folder is already set in your system path.
6. Verify the installation was successful by running terraform --version.
Automating an AWS EC2 Instance with Terraform
Now that you have installed Terraform, you can begin using it. In this post, I'm going to demonstrate building with a simple AWS EC2 instance. But know Terraform can provision hundreds of different types of infrastructure.
To get started, you'll first need a directory to run the Terraform scripts from. It's important to have a separate directory for each environment. At the time I'm writing this, Terraform doesn't have a way to filter what it runs. It will run every script in your current working directory.
Setting Up a TF Script
- In your cmd or PowerShell console ran as administrator, run
mkdir hello-terraformthencd ./hello-terraform - Once you have a directory, you'll need a Terraform script. Below is an example of one you can use. This is a typical Terraform script using the AWS provider to create an AWS instance resource.
If you'd like the entire script, copy it below. If you want to understand what this script is doing, read on below.
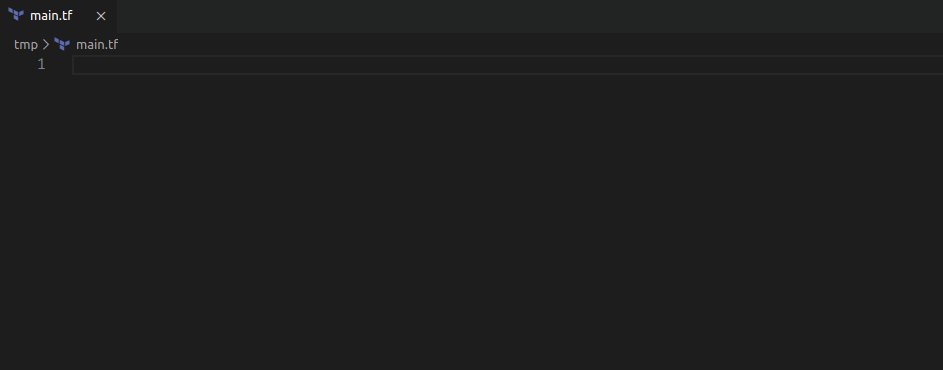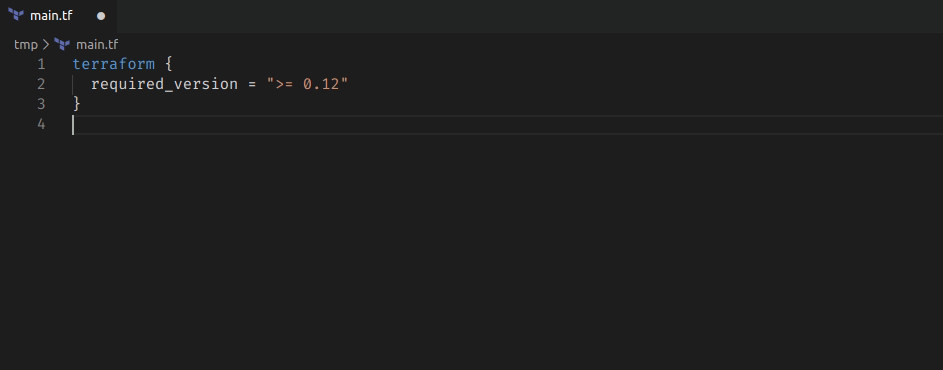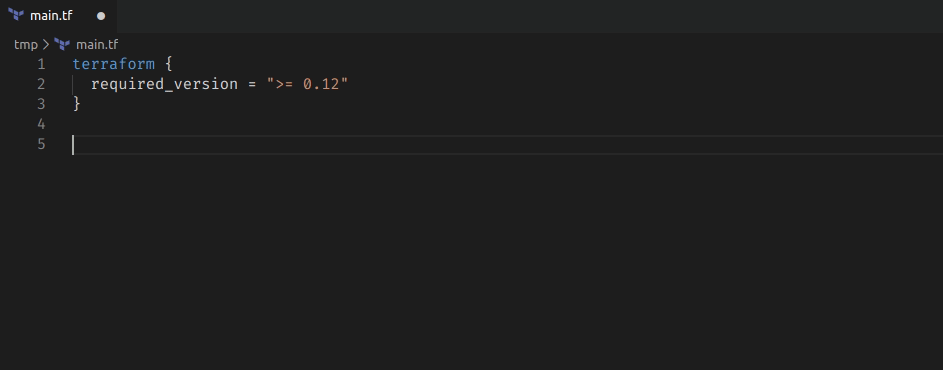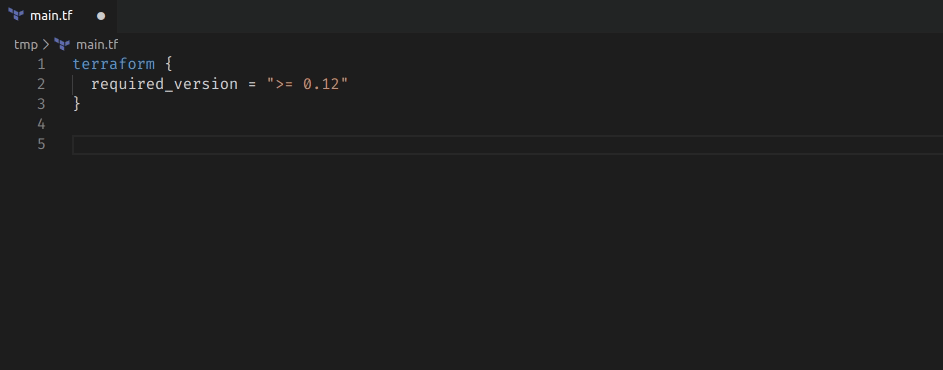
3. Save the script above as main.tf in your working directory.
Visual Studio Code Vs Visual Studio
Understanding TF Scripts
Before you go any further, look at the block below and what it's declaring.
Visual Studio Code Snippets
This block tells Terraform what provider to use. There are providers for all the major cloud vendors, as well as some on-prem vendors. If you're more advanced and you know how to write Golang, you can also write your own provider.
This block tells Terraform to use the AWS provider and access keys in the ~/.aws/credentials file under the profile name default. This file gets created when you setup the AWS CLI with aws config command as stated in the prerequisites.
It's also worth noting that ~/ is shorthand for the current user's directory. If you're coming from a Windows background, this is equal to as $env:USERPROFILE or %USERPROFILE%. But Terraform does not support that notation at the time of writing.
The next block below describes an EC2 Instance, and what to build it with. If you take a look at the Terraform documentation for aws_instance, you can see some parameters are required; some are optional. In this case, the required parameters are the AMI ID (ami-07d0cf3af28718ef8) for Ubuntu 18.04 LTS and t2.micro for the instance type.
By passing a tag block with the key Name and the value HelloTerraform, this tag will also get assigned to the instance that gets created. This is optional.
Building the AWS EC2 Instance: Testing
Now that the script is set up, call it by running terraform init from your working directory. This will pull down all the dependencies and provider into a folder named .terraform. If all goes well, you should get something like this:
Before you make any changes, Terraform allows you to see what will be created by running terraform plan. Here is what that will output:
Building the AWS EC2 Instance: Creating
Visual Studio Code Terraform Init
Now you're ready to run it for yourself by running terraform apply. Below you will see output like terraform plan, but with an added prompt to confirm that you actually want to apply these changes.
Visual Studio Code Terraform 12
Once you type ‘yes', Terraform will start provisioning the instance by calling the AWS APIs with the access key in your credentials file. This may take some time. Once finished, you'll see something like below:
Destroying the AWS EC2 Instance
Once you're done with the test environment, you can destroy the instance.
In your cmd/PowerShell console, type terraform destroy. Like the apply command, you'll see a list of resources Terraform is going to destroy then a prompt before actually destroying them.
Visual Studio Code Terraform 12
Once you type yes, Terraform will start destroying the instance and confirm when it's finished.
Summary
Now you know the many different ways to install and run Terraform on Windows. In this post, I covered a single-use case of configuring an AWS EC2 instance. Through that demonstration, you learned how to understand and interpret a Terraform file and what output Terraform returns when running. You then created and destroyed the instance, all from your cmd/PowerShell console.
By now, you should have a better understanding of how Terraform works, and how to get started with it in your own environment. Happy Terraforming!

